How to Choose the Right PCB Assembly for Industrial Automation
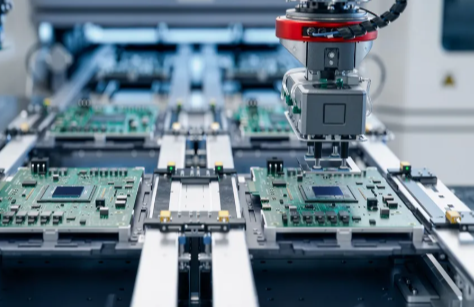
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape, printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the backbone of nearly every automated system. From robotic arms on production lines to telecommunications infrastructure, PCBs power the brain of machines. As demand for smarter, faster, and more reliable systems grows, choosing the right PCB assembly partner becomes critical. Companies like Industrial automation PCB assembly specialize in advanced industrial automation PCB assembly solutions that meet the evolving needs of modern industries.
Whether you’re designing equipment for high-frequency applications or building complex multi-layer boards for industrial robotics, this guide will help you navigate the key factors when selecting a PCB assembly partner and product type.
The Role of PCB Assembly in Industrial Automation
Industrial automation relies on a seamless flow of data, energy, and control signals—functions made possible by the complex design of printed circuit boards. PCB assemblies serve as the core foundation for:
Motor controllers
Power supply units
Sensor modules
Communication interfaces
Programmable logic controllers (PLCs)
Embedded systems and microcontrollers
Every component of a factory’s automation system must perform with precision and durability. That’s why PCB assembly in this sector requires not just quality—but reliability under pressure.
Key Requirements for Automation-Grade PCB Assemblies
PCB assemblies for industrial automation are often exposed to extreme environments—heat, vibration, chemical exposure, and electrical noise. To operate flawlessly, they must be engineered with several critical design considerations in mind.
1. High Reliability Components
Industrial systems can’t afford downtime. Boards must include industrial-grade capacitors, resistors, and ICs rated for extended temperature ranges and longer life cycles.
2. Signal Integrity
In high-speed automation environments—especially with robotics or data transmission—signal interference can lead to erratic behavior. High-frequency PCB materials (like PTFE or Rogers laminates) are essential to ensure clean, uninterrupted signals.
3. Durability and Environmental Resistance
PCBs may be subjected to moisture, chemicals, dust, and mechanical stress. To combat this:
Use conformal coatings or encapsulation
Opt for Rigid-Flex PCBs in applications where flexibility is required
Ensure PCB finishes like ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) for corrosion resistance
4. Thermal Management
Industrial environments often run hot—literally. PCBs should integrate thermal vias, copper pours, or even metal-core PCB substrates to manage heat effectively.
Types of PCB Solutions for Automation
As automation evolves, so does the need for specialized PCBs. Let’s break down some of the most common and advanced options available:
✅ Rigid PCBs
The industry standard, ideal for most control units, interface modules, and power boards. They offer high component density and are easy to fabricate in multiple layers.
✅ Flex and Rigid-Flex PCBs
These are essential for compact systems with space or movement constraints, such as robotic joints or foldable machinery. Flex PCBs reduce connector count, improve reliability, and save weight.
✅ High-Frequency PCBs
Used in applications that demand rapid signal transmission—telecom base stations, RF communication, and industrial sensors. These PCBs require low-loss materials and precise impedance control.
✅ Multilayer PCBs
Perfect for complex automation systems that require multiple functions integrated on one board—like power control, communication, and data processing.
Applications of PCBs in Industrial Automation
Here’s where industrial automation PCB assembly truly shines—across a wide variety of sectors:
⚙️ Robotics
From robotic arms on assembly lines to autonomous inspection systems, robotics depend on high-reliability PCBs for:
Motor control
Power conversion
Sensor data processing
AI-enabled decision-making modules
Telecommunications
Switching systems, base stations, and data transmission equipment rely on high-frequency PCBs to manage fast, consistent data flow.
Smart Manufacturing Systems
Smart factories use PCBs in:
Programmable logic controllers (PLCs)
Human-machine interfaces (HMIs)
Wireless communication modules
Real-time monitoring devices
Industrial Power Supplies
Stable power delivery is non-negotiable. PCBs are used in:
AC/DC converters
Inverters
Battery management systems
Voltage regulators
Why Partnering with a PCB Specialist Matters
Choosing the right manufacturer isn’t just about who can print and solder components—it’s about who understands the application and environment your board will serve in.
Here’s why manufacturers like Global Well PCBA stand out:
🔧 End-to-End Capabilities
From PCB fabrication to assembly, component sourcing, and testing, Global Well offers full-service solutions—reducing time-to-market and vendor risks.
Engineering Expertise
Their team offers design-for-manufacturing (DFM) support, layout optimization, and guidance on stack-up configuration and component placement.
Advanced Manufacturing Technology
SMT and through-hole capabilities
X-ray inspection, AOI, and ICT testing
Cleanroom assembly for sensitive components
Compliance with IPC-A-610 and ISO standards
Global Reach, Local Support
Despite being based in China, globalwellpcba.com serves international clients with English-language support and efficient shipping.
Common Challenges in Automation PCB Projects—and How to Solve Them
Even seasoned engineers face hurdles when designing or sourcing PCBs for automation. Here are a few issues and how to mitigate them:
⚠️ Component Obsolescence
Industrial systems often have long product life cycles. Always choose a vendor that supports long-term component sourcing or offers drop-in replacements.
⚠️ EMI/EMC Issues
High-speed and high-power signals can create electromagnetic interference. Use ground planes, shielding, and filtered connectors to maintain signal integrity.
⚠️ Assembly Errors
Poor solder joints, misalignment, or incorrect placements can lead to system failures. Choose a partner with rigorous quality control and automated inspection tools.
⚠️ Inadequate Testing
Skip this, and you’re flying blind. Insist on ICT (In-Circuit Testing), functional testing, and burn-in tests to validate reliability.
Read Also: Using Motion Graphics as a Branding Tool for Corporate Campaigns
The Future of PCBs in Industrial Automation
The automation industry is only getting smarter. With the rise of Industry 4.0, IoT-enabled devices, AI-powered robotics, and real-time factory analytics, PCBs will become even more critical—and more complex.
Expect to see trends such as:
More use of HDI (High-Density Interconnect) PCBs for space-saving designs
Integration of sensors directly on the board
Advanced materials to handle higher data rates and thermal loads
AI-assisted PCB design to reduce development time
Staying ahead in this space means working with manufacturers that innovate alongside you—providing the flexibility and technical know-how to support your vision.
Conclusion
Choosing the right PCB solution for industrial automation isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a strategic one. Whether you’re building advanced robotics, powering telecommunications systems, or enabling smarter manufacturing, the right PCB partner can make or break your project.
With advanced offerings like Rigid-Flex, High-Frequency, and multilayer PCB assemblies globalwellpcba.com from Global Well PCBA delivers the durability, precision, and support needed for mission-critical systems. Their expertise ensures you get reliable performance, quick turnaround, and top-notch quality—helping you stay competitive in the ever-evolving world of automation.